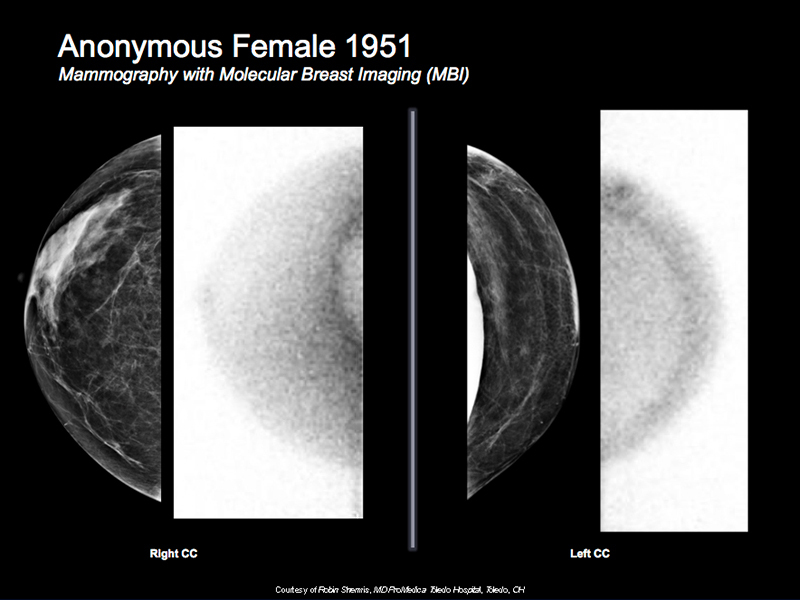
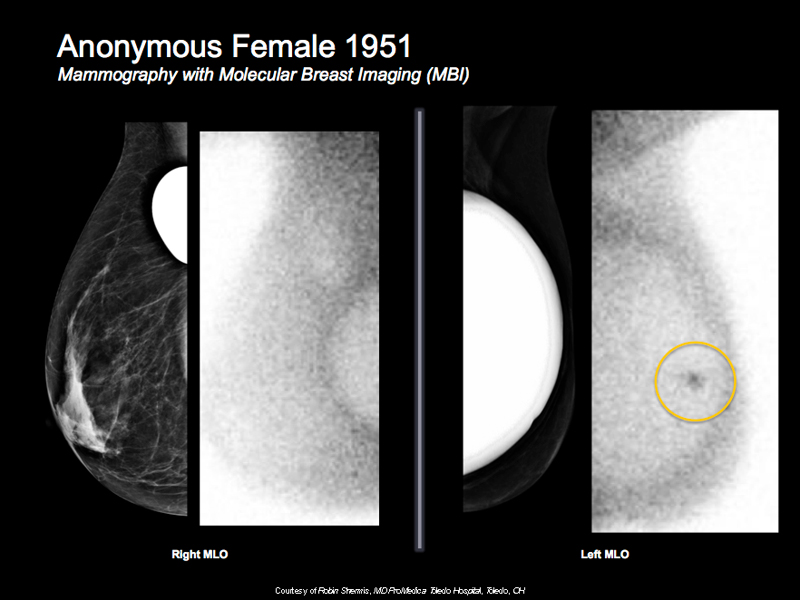
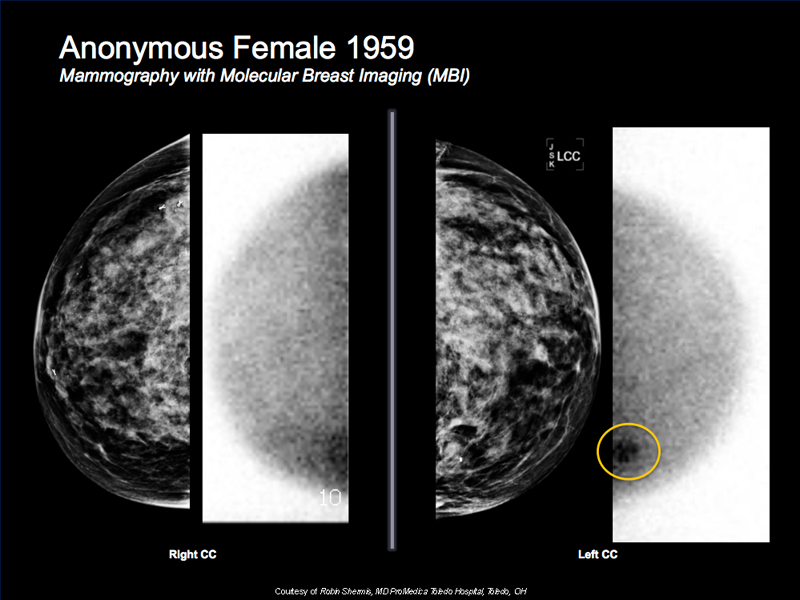
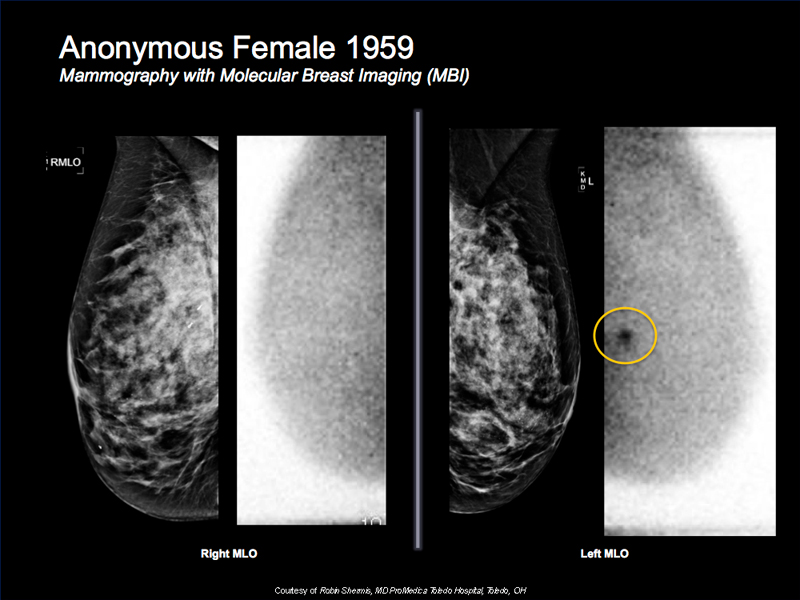
The Mayo Clinic recently published a prospective breast cancer detection case study in the American Journal of Roentgenology involving 1,585 dense breast women, finding that combination of MBI/mammography found nearly 400% times more invasive cancers versus mammography alone, while also resulting in 50% reduction in biopsy rates.1
Of the cancers detected with MBI, and missed by mammography, lesions as large as 4cm were included. Additionally, over 80% of the invasive cancers identified with MBI, but missed by mammography, were still at the local stage (i.e., ‘node-negative’) where treatment options and prognosis is optimal.1
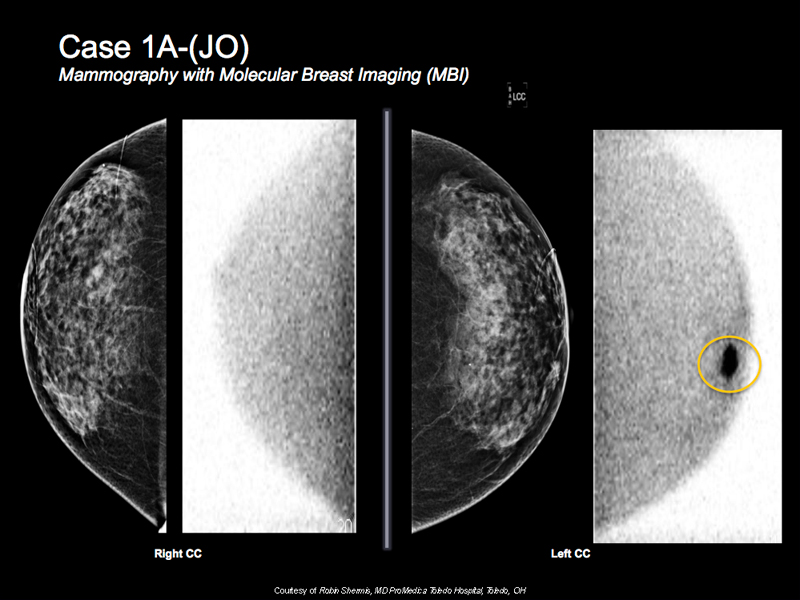
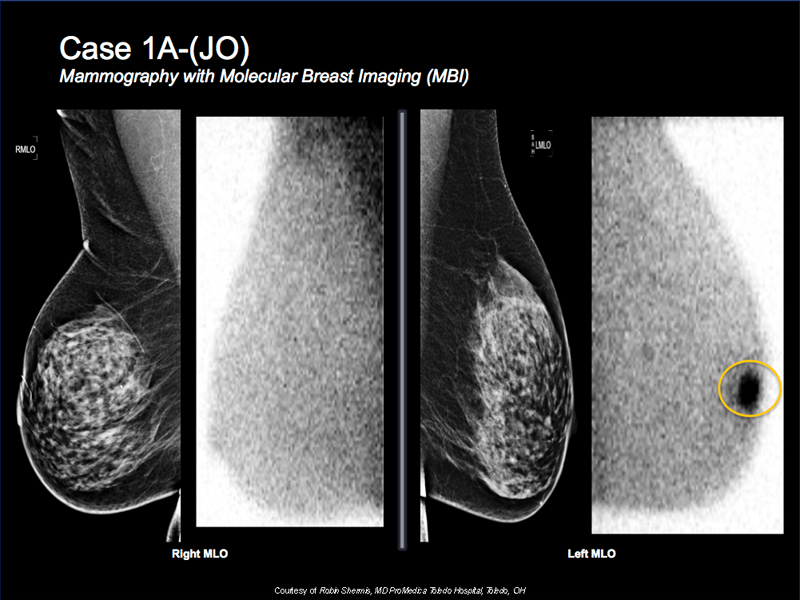
Breast Cancer Case Study 3: Case 1A-(JO)
- 67 y/o with dense mammogram
- MBI is done for additional surveillance and shows intense focal tracer activity on the left breast
- Correlative suspicious mass on targeted ultrasound
- Biopsy reveals invasive ductal carcinoma
- MBI, ultrasound and biopsy are done on same visit
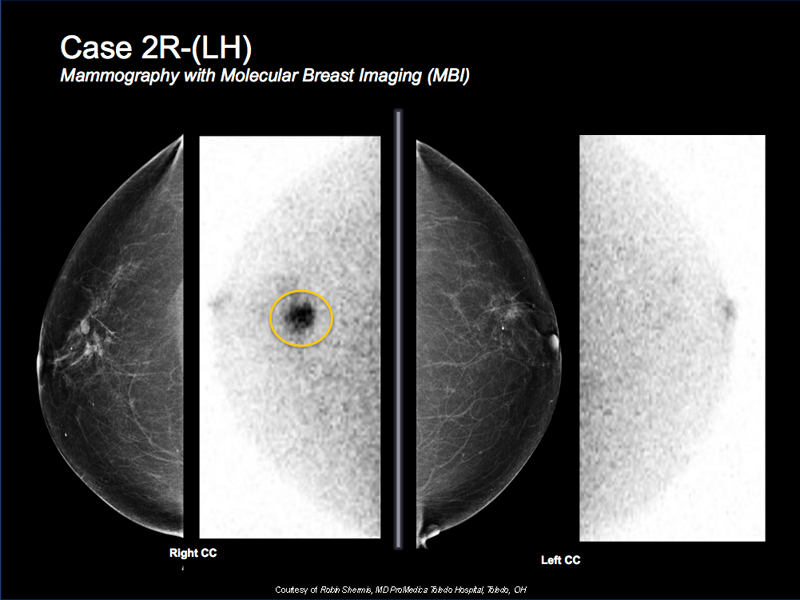
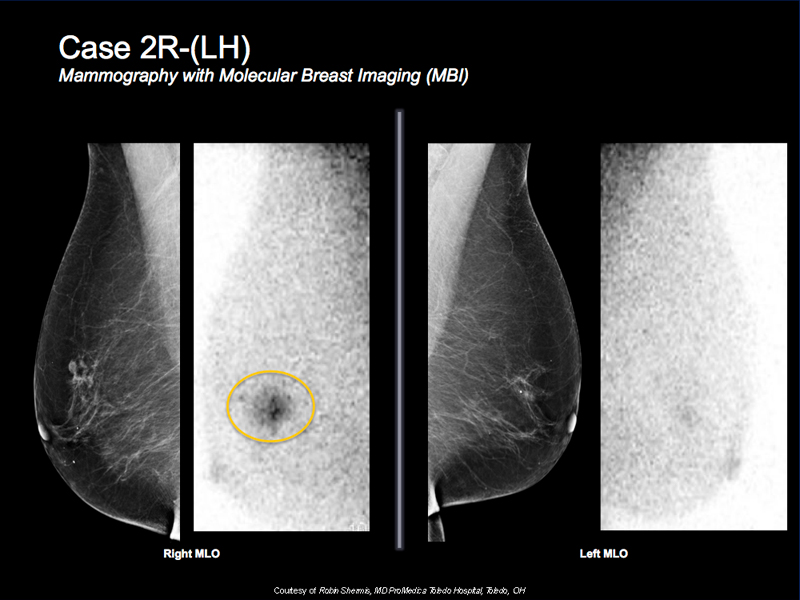
Breast Cancer Case Study 4: Case 2R-(LH)
- 70 y/o female with a known right breast cancer for preoperative evaluation due to dense mammogram
- Could not tolerate MRI
- MBI shows focal intense tracer activity corresponding to known cancer with some minimal surrounding post biopsy uptake
- There are no other suspicious findings
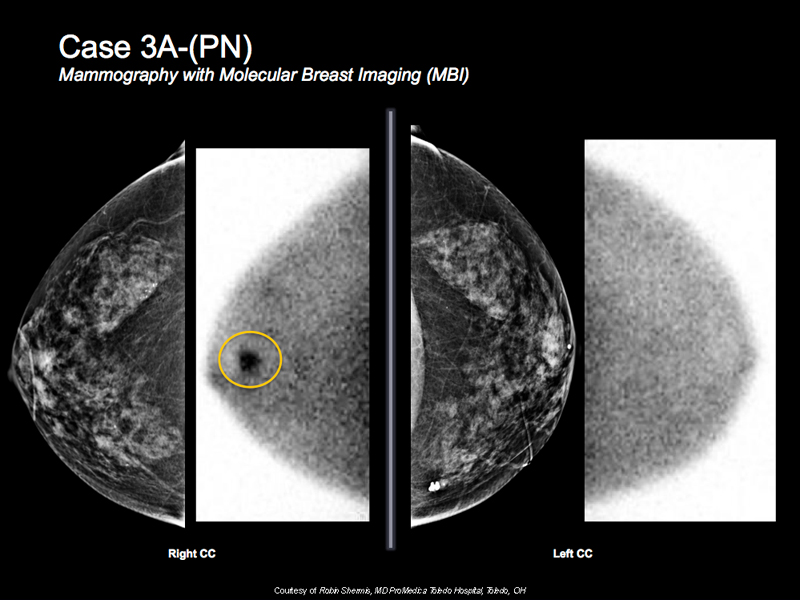
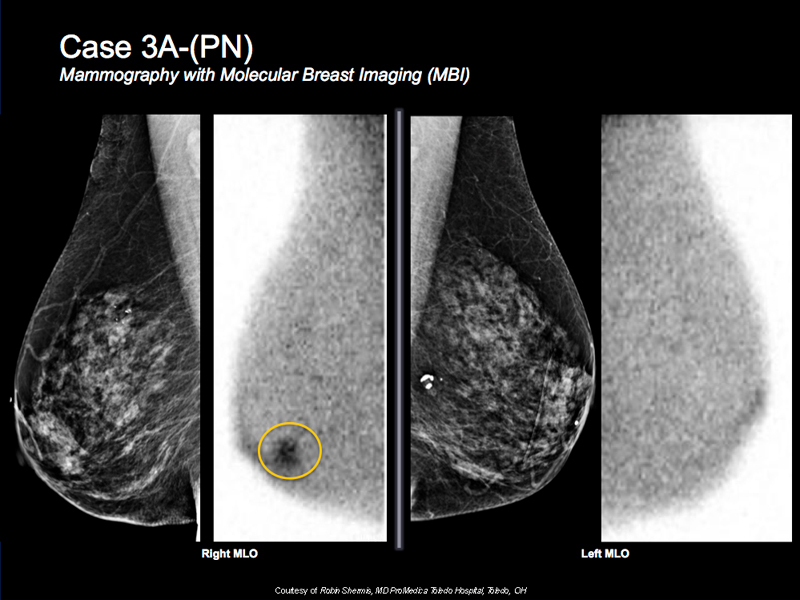
Breast Cancer Case Study 5: Case 3A-(PN)
- 81 y/o female. She is high risk
- Wanted more screening but could not tolerate MRI
- MBI shows intense focal tracer uptake in subareolar right breast
- Correlative suspicious mass under ultrasound
- Biopsy shows invasive ductal carcinoma
- MBI, ultrasound and biopsy done on the same visit
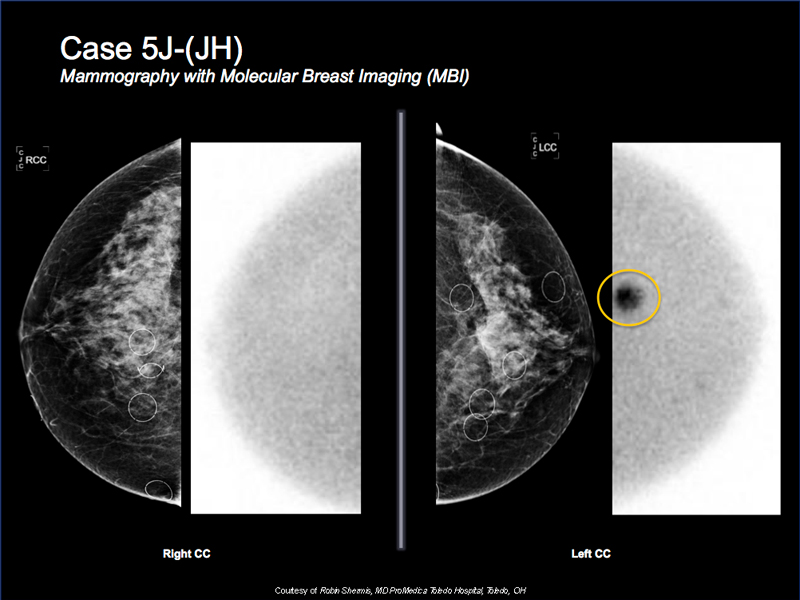
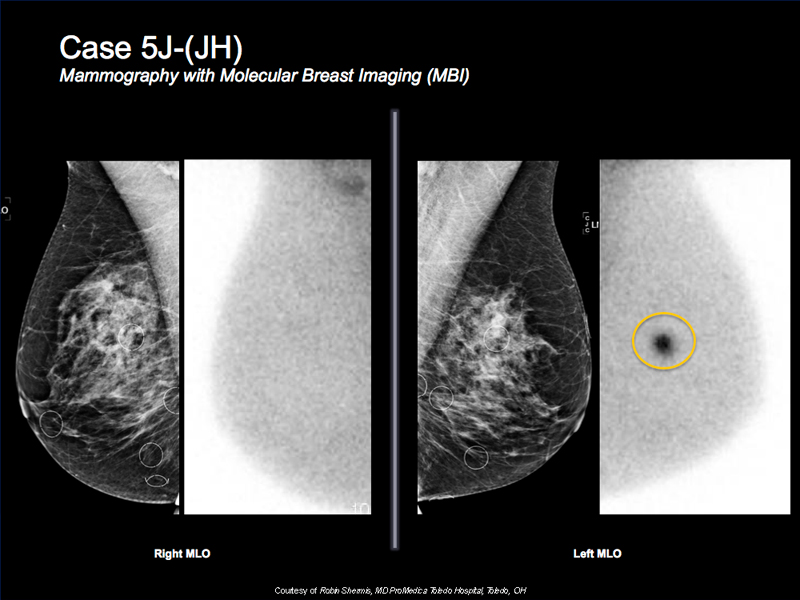
Breast Cancer Case Study 7: Case 5J-(JH)
- 53 y/o female with dense mammogram for additional screening
- Mammogram is very dense but negative
- MBI shows intense focal tracer accumulation at 2 o’clock
- Targeted ultrasound reveals a correlative suspicious solid mass
- Biopsy shows invasive ductal carcinoma
- MBI, ultrasound and biopsy all done at the same visit